Purpose of Continual Service Improvement
The purpose of the Continual Service Improvement stage of the life-cycle is to align IT services with changing business needs by identifying and implementing improvements to IT services that support business processes.These improvements activities support the life-cycle approach through service strategy, service design, service transition and service operation. CSI is always seeking ways to improve service effectiveness, process effectiveness and cost effectiveness.
The value delivered by Continual Service Improvement to the business:
- Gradual and continual improvement in service quality
- Ensure that IT services remain continuously aligned to business requirements
- Result in gradual improvements in cost effectiveness through a reduction in costs
- Identifying opportunities for improvement in all lifecycle stages and processes
- Identifying opportunities for improvements in organizational structures, resourcing capabilities, partners, technology, staff skills and training, and communications
Continual Service Improvement Processes
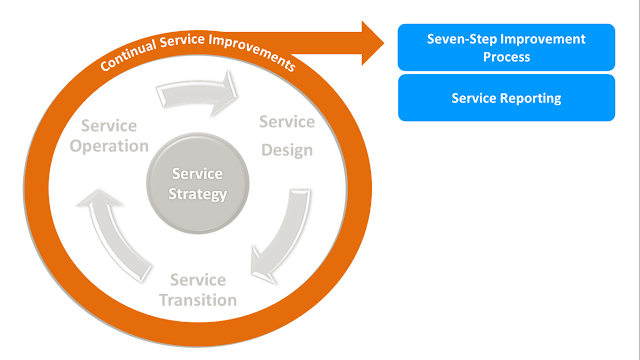
There are four main processes under Continual Service Improvement Strategy stage of ITIL lifecycle:- Seven-Step Improvement Process
- Service Reporting process
Seven-Step Improvement Process provides a seven-stage
framework that helps to guide the improvement and correction of service
performance.
Service Reporting process helps to build a business-focused service reporting framework.
Service Reporting process helps to build a business-focused service reporting framework.